DITA is also known as Darwin Information Typing Architecture. It is a standard way of organizing and producing materials that is based on XML. It is frequently used in technical documentation to arrange and recycle contents effectively across several outputs and ensure consistency.
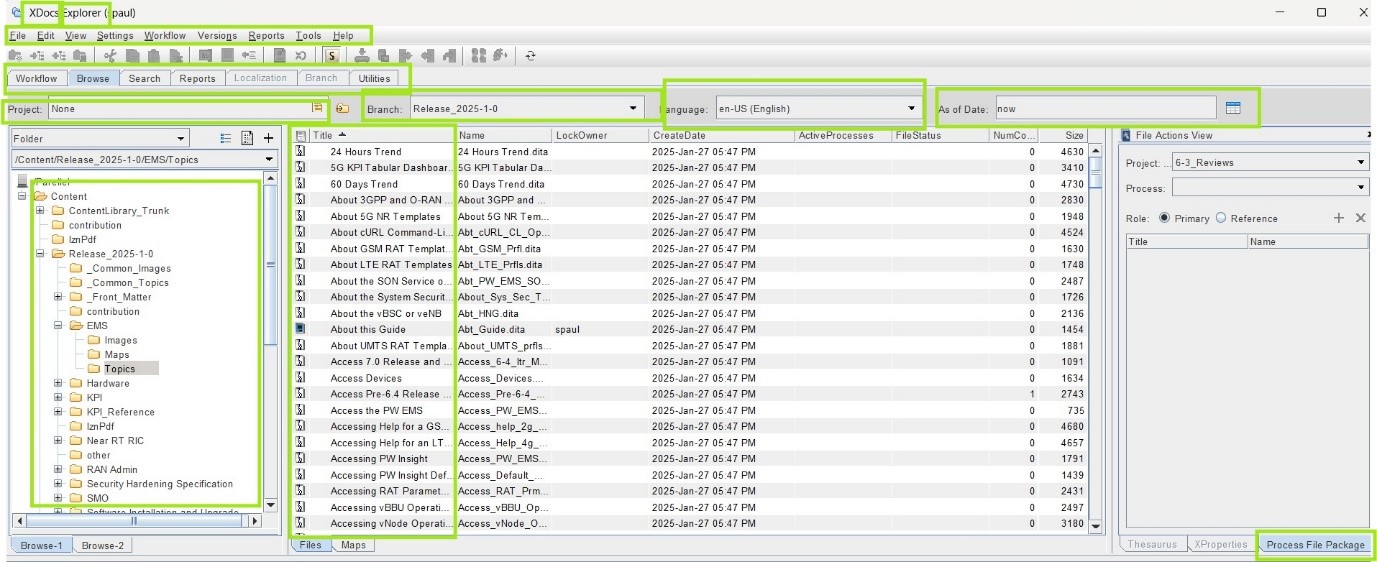
An explanation of DITA and how structured content functions within it is discussed below:
Key Features
1. Modular Content:
Generally, DITA organizes content around small modular components or ‘topics’ that can be reused. Each topic would be referring to one specific subject or task.
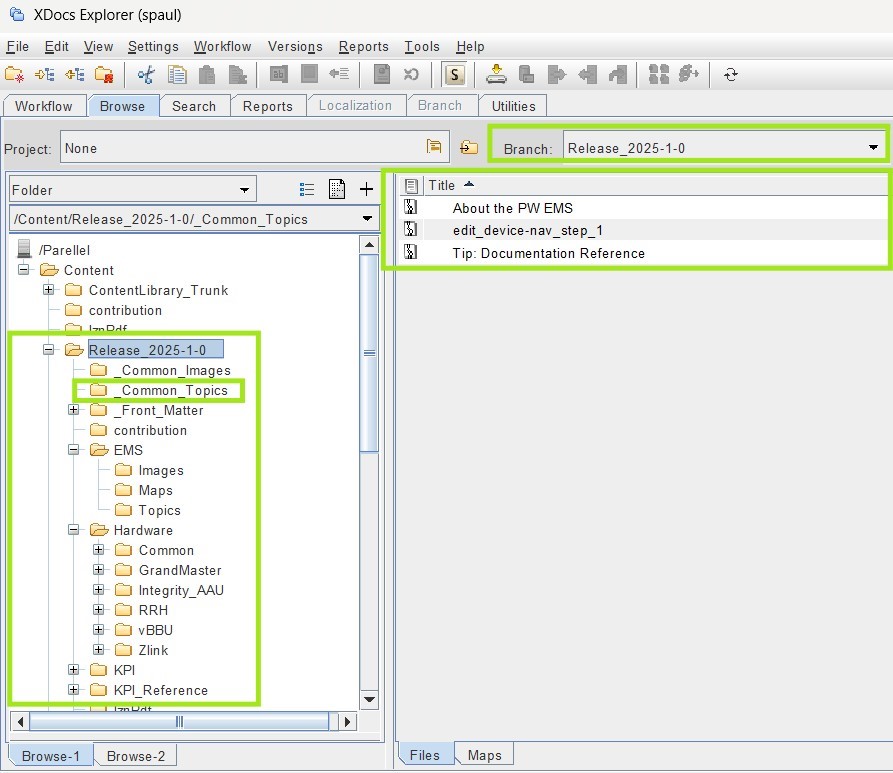
2. Topic types:
- Concept: A site for notions and theories or mere background.
- Task: Stepwise instructions.
- Reference: This information means supplying really deep structured information such as tables, specifications, or lists.
- General Topic: This structure is really quite flexible for anything else.

3. Maps and Hierarchy:
DITA Maps define topic linkages and a hierarchy between them, which in turn define a document structure. It serves as a blueprint to manufacture deliverables like manuals, websites, or PDFs, which will be created according to this map.

4. Specialization:
No specialization of the topic types and elements is allowed by the DITA standard, which, in turn, provides the mean for DITA standard to be specialized for industries and types of content such.
5. Metadata:
The DITA attribute specifies metadata that governs content filtering, reuse, and conditional publishing (for example, filtering content for different audiences or different product versions).
6. Content Reuse:
DITA’s content reusability enables:
- Topic Reuse: The same topic being referenced in multiple maps.
- Content Reuse: Including content from one topic into another using conrefs or content references.
- Keyrefs: Assigning keys describes content for linking and reuse.
7. The Actual Publishing: Publishing tools and the DITA Open Toolkit (DITA-OT) can take the content written in DITA and convert it to different outputs such as PDF, HTML, ePub, etc.